Within the final decade, the UK has had 4 considerably totally different units of know-how priorities, and a brief, however disruptive, interval, the place such prioritisation was opposed on precept. This 3500 phrase piece seems at this historical past of instability in UK innovation coverage, and suggests some rules of consistency and readability which could give us some extra stability within the decade to come back. A PDF model might be downloaded right here.
Introduction
The issue of coverage churn has been recognized in various coverage areas as a barrier to productiveness development within the UK, and science and innovation coverage isn’t any exception to this. The UK can’t do every thing – it represents lower than 3% of the world’s R&D assets, so it must specialise. However latest governments haven’t discovered it straightforward to determine the place the UK ought to put its focus, after which persist with these selections.
In 2012 this the then Science Minister, David Willetts, launched an initiative which recognized 8 precedence applied sciences – the “Eight Nice Applied sciences”. Willetts mirrored on the destiny of this initiative in a very attention-grabbing paper printed final yr. In brief, whereas there was consensus on the necessity for the UK to focus (except for one brief interval), the areas of focus have been topic to frequent change.
Substantial adjustments in course for know-how coverage have occurred even if we’ve had a single political celebration in energy since 2010, with specific instability since 2015, within the interval of Conservative majority authorities. Since 2012, the common life-span of an innovation coverage has been about 2.5 years. Beneath the headline adjustments, it’s true that there have been some continuities. However given the lengthy time-scales wanted to ascertain analysis programmes and to hold them by to their outcomes, this instability makes it totally different to implement any sort of coherent technique.
Shifting Priorities: from “Eight Nice Applied sciences”, by “Seven Know-how Households”, to “5 Essential Applied sciences”
Desk 1 summarises the assorted precedence applied sciences recognized in authorities coverage since 2012, grouped in a method which finest brings out the continuities (click on to enlarge).
The “Eight Nice Applied sciences” had been launched in 2012 in a speech to the Royal Society by the then Chancellor of the Exchequer, George Osborne; a paper by David Willetts expanded on the rationale for the alternatives . The 2014 Science and Innovation Coverage endorsed the “Eight Nice Applied sciences”, with the addition of quantum know-how, which, following an intensive lobbying train, had been added to the record within the 2013 Autumn Assertion.
2015 introduced a majority Conservative authorities, however continuity within the places of work of Prime Minister and Chancellor of the Exchequer didn’t translate into continuity in innovation coverage. The brand new Secretary of State within the Division of Enterprise, Innovation and Expertise was Sajid Javid, who dropped at the publish a Thatcherite mistrust of something that smacked of business technique. The primary sufferer of this world-view was the innovation company Innovate UK, which was subjected to important cut-backs, inflicting lasting injury.
This interlude didn’t final very lengthy – after the Brexit referendum, David Cameron’s resignation and the premiership of Theresa Could, there was an elevated urge for food for intervention within the economic system, coupled with a rising consciousness and acknowledgement of the UK’s productiveness drawback. Greg Clark (a former Science Minister) took over at a renamed and expanded Division of Enterprise, Power and Industrial Technique.
A White Paper outlining a “fashionable industrial technique” was printed in 2017. Though it nodded to the “Eight Nice Applied sciences”, the main target shifted to 4 “missions”. Cash had already been put aside within the 2016 Autumn Assertion for an “Industrial Technique Problem Fund” which might assist R&D in assist of the priorities that emerged from the Industrial Technique.
2019 noticed one other change of Prime Minister – and one other election, which introduced one other Conservative authorities, with a a lot better majority, and a relatively interventionist manifesto that promised substantial will increase in science funding, together with a brand new company modelled on the USA’s ARPA, and a promise to “focus our efforts on areas the place the UK can generate a commanding lead within the industries of the long run – life sciences, clear power, area, design, computing, robotics and synthetic intelligence.”
However the “fashionable industrial technique” didn’t survive lengthy into the brand new administration. The brand new Secretary of State was Kwasi Kwarteng, from the wing of the celebration with an ideological aversion to industrial technique. In 2021, the economic technique was outmoded by a Treasury doc, the Plan for Progress, which, whereas putting robust emphasis on the significance of innovation, took a way more sector and know-how agnostic method to its assist. The Plan for Progress was supported by a brand new Innovation Technique, printed later in 2021. This did establish a brand new set of precedence applied sciences – “Seven Know-how Households”.
2022 was the yr of three Prime Ministers. Liz Truss’s hard-line free market place was actually unfriendly to the idea of business technique, however in her 44 day tenure as Prime Minister there was not sufficient time to make any important adjustments in course to innovation coverage.
Rishi Sunak’s Premiership introduced one other important improvement, within the type of a equipment of presidency change reflecting the brand new Prime Minister’s enthusiasm for know-how. A brand new division – the Division for Innovation, Science and Know-how – meant that there was now a cupboard stage Secretary of State targeted on science. One other important evolution within the profile of science and know-how in authorities was the growing prominence of nationwide safety as a driver of science coverage.
This had begun within the 2021 Built-in Evaluation , which was an try and set a single imaginative and prescient for the UK’s place on the planet, protecting safety, defence, improvement and overseas coverage. This elevated “Sustaining strategic benefit by science and know-how” as certainly one of 4 overarching rules. The disruptions to worldwide provide chains through the covid pandemic, and the 2022 invasion of Ukraine by Russia and the next giant scale European land conflict, raised the problem of nationwide safety even larger up the political agenda.
A brand new division, and a modified set of priorities, produced a brand new 2023 technique – the Science & Know-how Framework – taking a techniques method to UK science & know-how . This included a brand new set of know-how priorities – the “5 vital applied sciences”.
Thus in a single decade, we’ve had 4 considerably totally different units of know-how priorities, and a brief, however disruptive, interval, the place such prioritisation was opposed on precept.
Continuities and discontinuities
There are some continuities in substance in these know-how priorities. Quantum know-how appeared round 2013 as an addendum to the “Eight Nice Applied sciences”, and survives into the present “5 Essential Applied sciences”. Problems with nationwide safety are a giant driver right here, as they’re for a lot bigger scale programmes within the USA and China.
In a few different areas, identify adjustments conceal substantial continuity. What was known as artificial biology in 2012 is now encompassed within the subject of engineering biology. Synthetic Intelligence has come to excessive public prominence at present, however it’s a pure evolution of what was known as massive knowledge, pushed by technical advances in machine studying, extra pc energy, and greater knowledge units.
Priorities in 2017 had been outlined as Grand Challenges, not Applied sciences. The language of challenges is taken up within the 2021 Innovation Technique, which proposes a set of Innovation Missions, distinct from the precedence know-how households, to deal with main societal challenges, in areas akin to local weather change, public well being, and intractable ailments. The 2023 Science and Know-how Framework, nonetheless, describes investments in three of the 5 Essential Applied sciences, engineering biology, synthetic intelligence, and quantum applied sciences, as “know-how missions”, which appears to make use of the time period in a considerably totally different sense. There may be room for extra readability about what is supposed by a grand problem, a mission, or a know-how, which I’ll return to under.
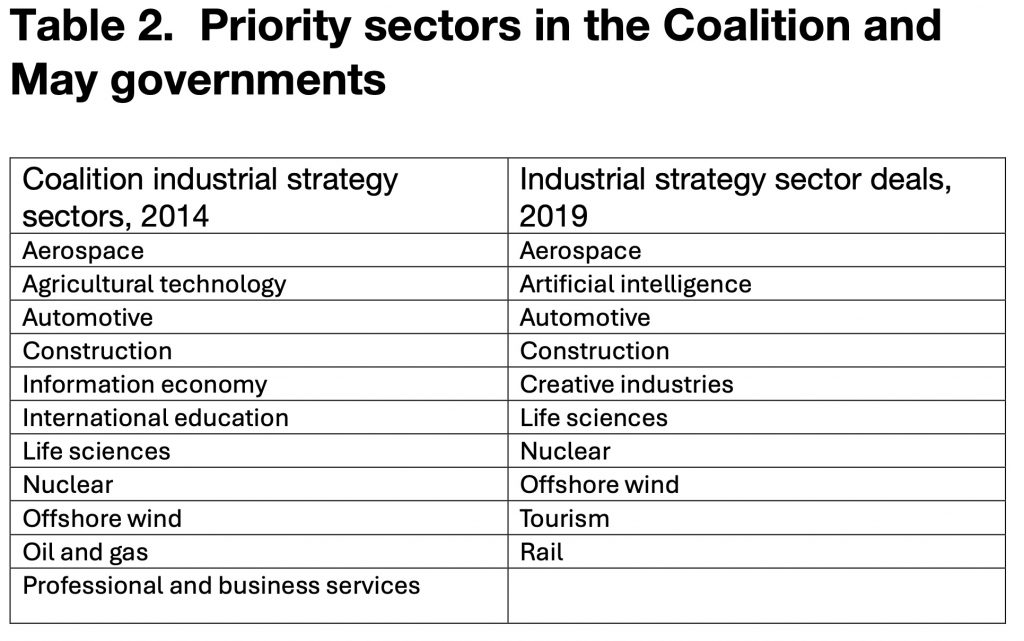
One other distinction that isn’t all the time clear is between applied sciences and trade sectors. Each the Coalition and the Could governments had industrial methods that explicitly singled out specific sectors for assist, together with by assist for innovation. These are listed in desk 2. However it’s controversial that a minimum of two of the Eight Nice Applied sciences – agritech, and area & satellites – can be higher regarded as trade sectors relatively than applied sciences.
Desk 2 – industrial technique sectors, as outlined by the Coalition, and the Could authorities.
The sector method did underpin main utilized public/personal R&D programmes (such because the Aerospace Know-how Institute, and the Superior Propulsion Centre), and new R&D establishments, such because the Offshore Renewable Catapult Centre, designed to assist particular trade sectors. In the meantime, beneath the banner of Life Sciences, there may be continued express assist from the pharmaceutical and biotech trade, although right here there’s a lack of readability about whether or not the first aim is to advertise the well being of residents by innovation assist to the well being and social care system, or to assist pharma and biotech as excessive worth, exporting, industrial sectors.
However two of the 2023 “5 vital applied sciences” – semiconductors and future telecoms – are considerably new. Once more, these look extra like industrial sectors than applied sciences, and whereas nobody can doubt their strategic significance within the international economic system it isn’t apparent that the UK has a very robust comparative benefit in them, both within the dimension of the prevailing enterprise base or the size of the UK market (see my earlier dialogue of the background to a UK Semiconductor Technique).
The story of the final ten years, then, is a scarcity of consistency, not simply within the priorities themselves, however within the conceptual foundation for making the prioritisation – whether or not challenges or missions, trade sectors, or applied sciences.
From technique to implementation
How does one flip from technique to implementation: given a set of precedence sectors, what must occur to show these into analysis programmes, after which translate that analysis into industrial outcomes? An apparent level that nonetheless wants stressing, is that this course of has lengthy lead occasions, and this isn’t suitable with innovation methods which have a median lifetime of two.5 years.
To cite the latest Willetts evaluation of the enterprise case course of for scientific programmes: “One senior official estimated the time from an unique thought, arising in Analysis Councils, to execution of a programme at over two and a half years with 13 particular approvals required.” It might clearly be fascinating to chop a few of the paperwork that causes such delays, however it’s placing that the time taken to design and provoke a analysis programme is of the identical order as the common lifetime of an innovation technique.
One knowledge level right here is the destiny of the Industrial Technique Problem Fund. This was introduced within the 2016 Autumn Assertion, anticipating the 2017 Industrial Technique White Paper, and exists to assist translational analysis programmes in assist of that Industrial Technique. As we’ve seen, this technique was de-emphasised in 2019, and formally scrapped in 2021. But the analysis programmes set as much as assist it are nonetheless going, with cash nonetheless within the finances to be spent in FY 24/25.
In fact, a lot worthwhile analysis shall be being performed in these programmes, so the cash isn’t wasted; the issue is that such orphan programmes might not have any follow-up, as new programmes on totally different subjects are designed to assist the newest technique to emerge from central authorities.
Typically the timescales are such that there isn’t even an opportunity to operationalise one technique earlier than one other one arrives. The main public funder of R&D, UKRI, produced a 5 yr technique in March 2022 , which was underpinned by the seven know-how households. To operationalise this technique, UKRI’s constituent analysis councils produced a set of supply plans . These had been printed in September 2022, giving them a run of six months earlier than the arrival of the 2023 Science and Innovation Framework, with its new set of vital applied sciences.
A pure response of funding companies to this instability can be to determine themselves what finest to do, after which do their finest to retro-fit their ongoing programmes to new authorities methods as they emerge. However this is able to defeat the purpose of creating a technique within the first place.
The following ten years
How can we do higher over the following decade? We have to give attention to consistency and readability.
Consistency means having one technique that we persist with. If we’ve this, traders can believe within the UK, analysis establishments could make knowledgeable selections about their very own investments, and particular person researchers can plan their careers with extra confidence.
In fact, the technique ought to evolve, as sudden developments in science and know-how seem, and because the exterior surroundings adjustments. And it ought to construct on what has gone earlier than – for instance, there may be a lot of worth within the techniques method of the 2023 Science and Innovation Framework.
There must be readability on the premise for prioritisation. I feel you will need to be a lot clearer about what we imply by Grand Challenges, Missions, Business Sectors, and Applied sciences, and the way they differ from one another. With sharper definitions, we’d discover it simpler to ascertain clear standards for prioritisation.
For me, Grand Challenges set up the situations we’re working beneath. Some grand challenges would possibly embrace:
- Learn how to transfer our power economic system to a zero-carbon foundation by 2050;
- Learn how to create an reasonably priced and humane well being and social care system for an ageing inhabitants;
- Learn how to restore productiveness development to the UK economic system and cut back the UK’s regional disparities in financial efficiency;
- Learn how to preserve the UK secure and safe in an more and more unstable and hostile world.
One would hope that there was a large consensus in regards to the scale of those issues, although not everybody will agree, nor will it all the time be apparent, what one of the simplest ways of tackling them is.
Some would possibly refer to those overarching points as missions, utilizing the time period popularised by Mariana Mazzacuto , however I would favor to seek advice from a mission as one thing extra particular, with a way of timescale and a particular goal. The 1960’s Moonshot programme is commonly taken as an exemplar, although I feel the extra important mission from that interval was to create the power for the USA to land a half tonne payload anyplace on the earth’s floor, with an accuracy of some hundred meters or higher.
The essential characteristic of a mission, then, is that it’s a focused program to attain a strategic aim of the state, that requires each the mixing and refinement of current applied sciences and the event of latest ones. Defining and prioritising missions requires working throughout the entire of presidency, to establish the issues that the state must be solved, and which are tractable sufficient given affordable know-how foresight to be price attempting, and prioritising them.
The important thing questions for a judging missions, then, are, how a lot does the federal government need this to occur, how possible is it given foreseeable know-how, how effectively geared up is the UK to ship it given its industrial and analysis capabilities, and the way reasonably priced is it?
For supporting an trade sector, although, the questions are totally different. Sector assist is a part of an energetic industrial technique, and given the tendency of trade sectors to cluster in area, this has a robust regional dimension. The targets of business technique are largely financial – to boost the financial productiveness of a area or the nation – so the standards for choosing sectors must be primarily based on their significance to the economic system when it comes to the fraction of GVA that they provide, and their potential to enhance productiveness.
Up to now industrial technique has usually been pushed by the necessity to create jobs, however our present drawback is productiveness, relatively than unemployment, so I feel the important thing standards for choosing sectors must be their potential to create extra worth by the applying of innovation and the event of abilities of their workforces.
Along with the financial dimension, there might also be a safety facet to the selection, if there’s a cause to suppose that sustaining functionality in a selected sector is important to nationwide safety. The 2021 nationalisation of the metal forging firm, Sheffield Forgemasters, to safe the potential to fabricate vital elements for the Royal Navy’s submarine fleet, would have been unthinkable a decade in the past.
Industrial technique might contain assist for innovation, for instance by collaborative programmes of pre-competitive analysis. Nevertheless it must be broader than simply analysis and improvement; it could contain growing establishments and programmes for innovation diffusion, the harnessing of public procurement, the event of specialist abilities provision, and at a regional stage, the availability of infrastructure.
Lastly, on what foundation ought to we select a know-how to give attention to? By a know-how precedence, we seek advice from an rising functionality arising from new science, that could possibly be adopted by current trade sectors, or might create new, disruptive sectors. Right here an understanding of the worldwide analysis panorama, and the UK’s a part of that, is an important place to begin. Even the most recent know-how, to be applied, will depend on current industrial functionality, so the form of the prevailing UK industrial base does have to be taken account. Lastly, one shouldn’t underplay the significance of the imaginative and prescient of gifted and pushed people.
This isn’t to say that priorities for the entire of the science and innovation panorama have to be outlined when it comes to challenges, missions, and trade sectors.
A basic framework for abilities, finance, regulation, worldwide collaboration, and infrastructure – as set out by the latest Science & Innovation Framework – must underlie extra particular prioritisation. Sustaining the well being of the fundamental disciplines is vital to supply resilience within the face of the unanticipated, and you will need to be open to new developments and preserve agility in responding to them.
The start line for a science and innovation technique must be to understand that, fairly often, science and innovation shouldn’t be the place to begin. Science coverage isn’t the identical as industrial technique, though it’s usually used as a (less expensive) substitute for it. For challenges and missions, defining the targets should come first; solely then can one determine what advances in science and know-how are wanted to convey these in attain. Likewise, in a profitable industrial technique, shut engagement with the prevailing capabilities of trade and the calls for of the market are wanted to outline the areas of science and innovation that may assist the event of a selected trade sector.
As I confused in my earlier, complete, survey of the UK Analysis and Improvement panorama, underlying any lasting technique must be a settled, long-term view of what sort of nation the UK aspires to be, what sort of economic system it ought to have, and the way it sees its place on the planet.