Movement management is enabling new ranges of robotic precision. Supply: Adobe Inventory
Garnering a lot consideration as of late are industrial robots and their integration of movement elements and incorporation into workcells with different motion-based automated tools. Such robotic workcells additionally function conveyors, imaginative and prescient programs, and machines to automate particular duties.
So, what makes a movement system a robotic or machine? In different phrases, what’s the excellence between movement programs utilized in automated equipment and that taking the type of robots? The latter are able to routinely executing advanced and programmable (and particularly reconfigurable) motion sequences.
This definition is admittedly fairly obscure, and even the ISO 8373 definition might describe machines not normally thought of robots. It says a robotic is an “routinely managed multipurpose manipulator” reprogrammable in three or extra axes.
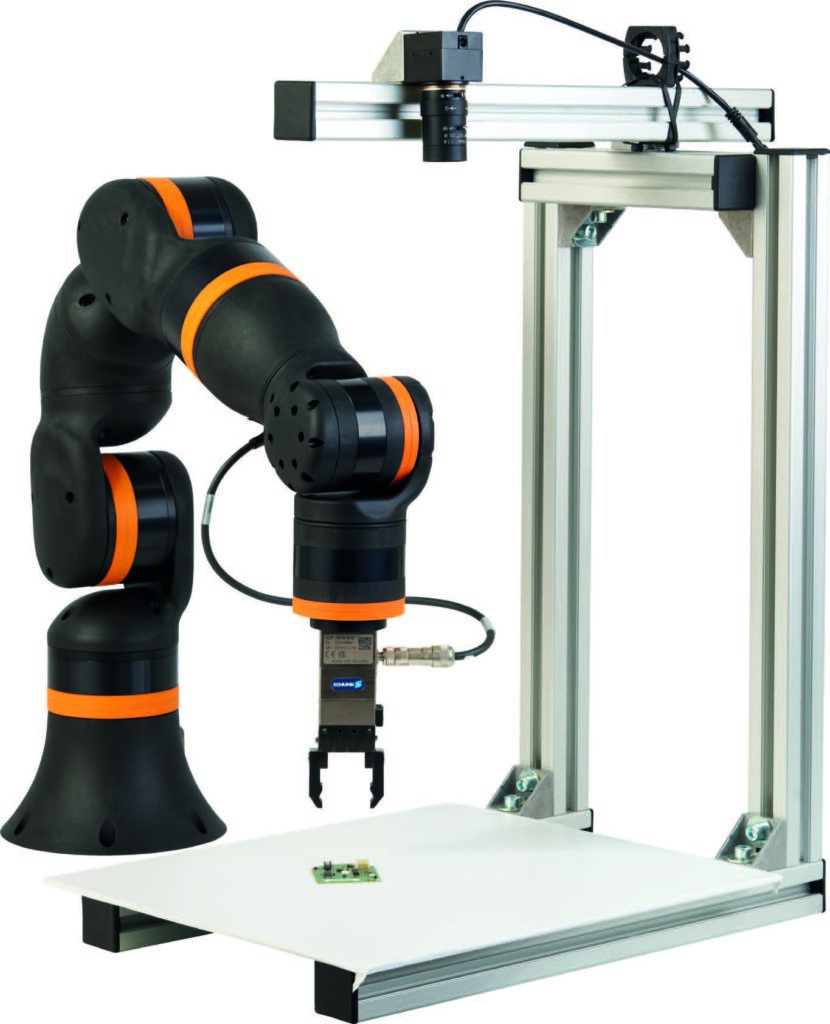

This igus setup options AI-powered machine imaginative and prescient.
In distinction with robots, machines equivalent to merchandising machines (to provide only one instance) are designed for a single well-defined use in a single mounted location. They will run duties on totally different workpieces however aren’t more likely to be reprogrammed for a number of functions. Machines solely serve the one well-defined use of dishing out bought merchandise.
Robotics within the type of Cartesian robotics additionally encompass assemblies of linear-motion elements equivalent to linear guides, ballscrews, and encoders — or pre-integrated actuators, and even linear motors as within the high-speed meeting proven under. However identical to articulated and SCARA robotics, these usually tend to serve numerous adaptive capabilities.

Typical applied sciences for every robotic kind
Actually, some gears, motors, and controls applied sciences are widespread to articulated and SCARA robotics in addition to Cartesian programs. These stationary programs — typically what’s implied in references to “industrial robots” — even share primary applied sciences with automated guided automobiles (AGVs).
Extra info on AGVs could be discovered at The Robotic Report, Automated Warehouse, and Design World. However methods differ for synchronizing multi-axis movement with robotic kinematics.
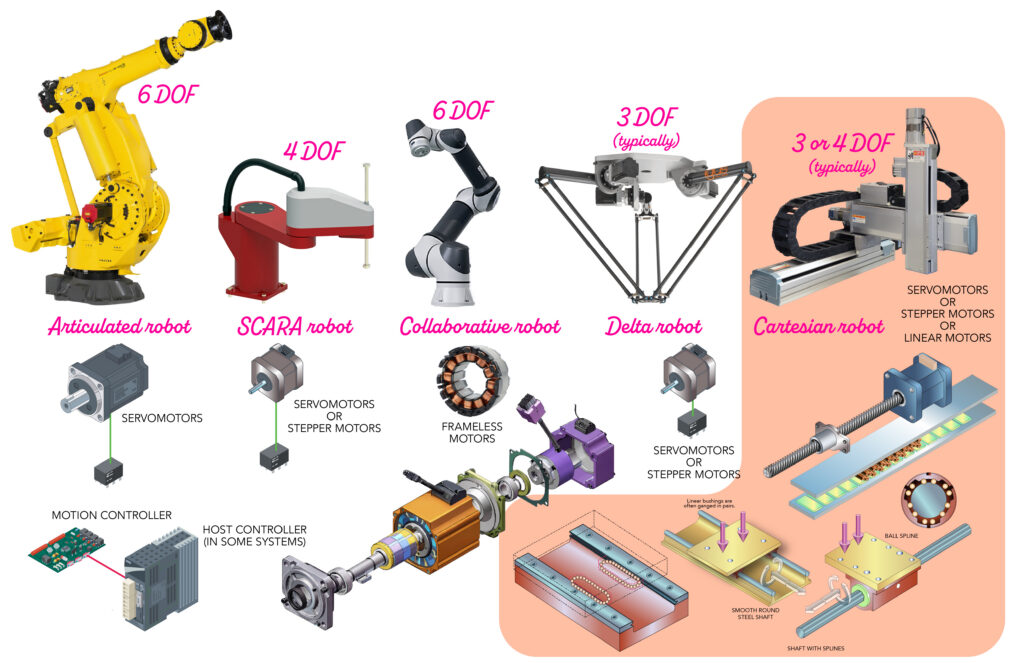
Associated: Main motion-control and actuation choices for robotics
The secret is decreasing latency, complexity, and price for materials dealing with, machine tending, and different setups that includes robotics alongside different varieties of movement programs.
Movement part suppliers = robotic suppliers
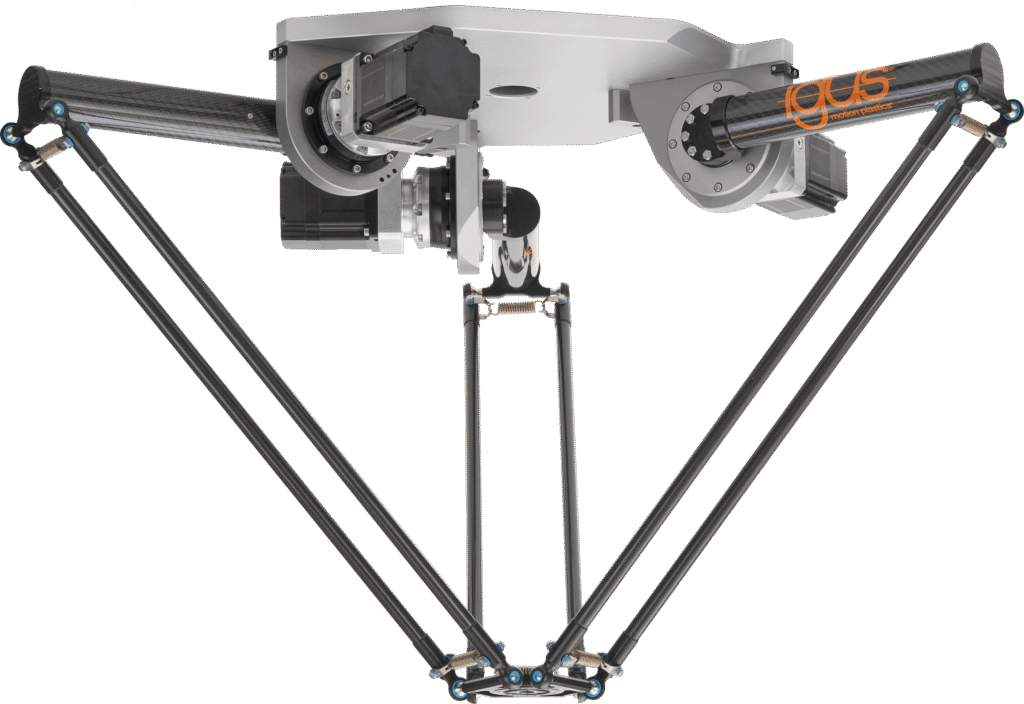
An RBTX three-DoF delta robotic. Supply: igus
As robotics are only a subset of movement system designs, it’s no surprise that many motion-component suppliers supply fully pre-integrated robots of their very own. Others help the design and integration of robotics with subsystems personalized to robotic operations.
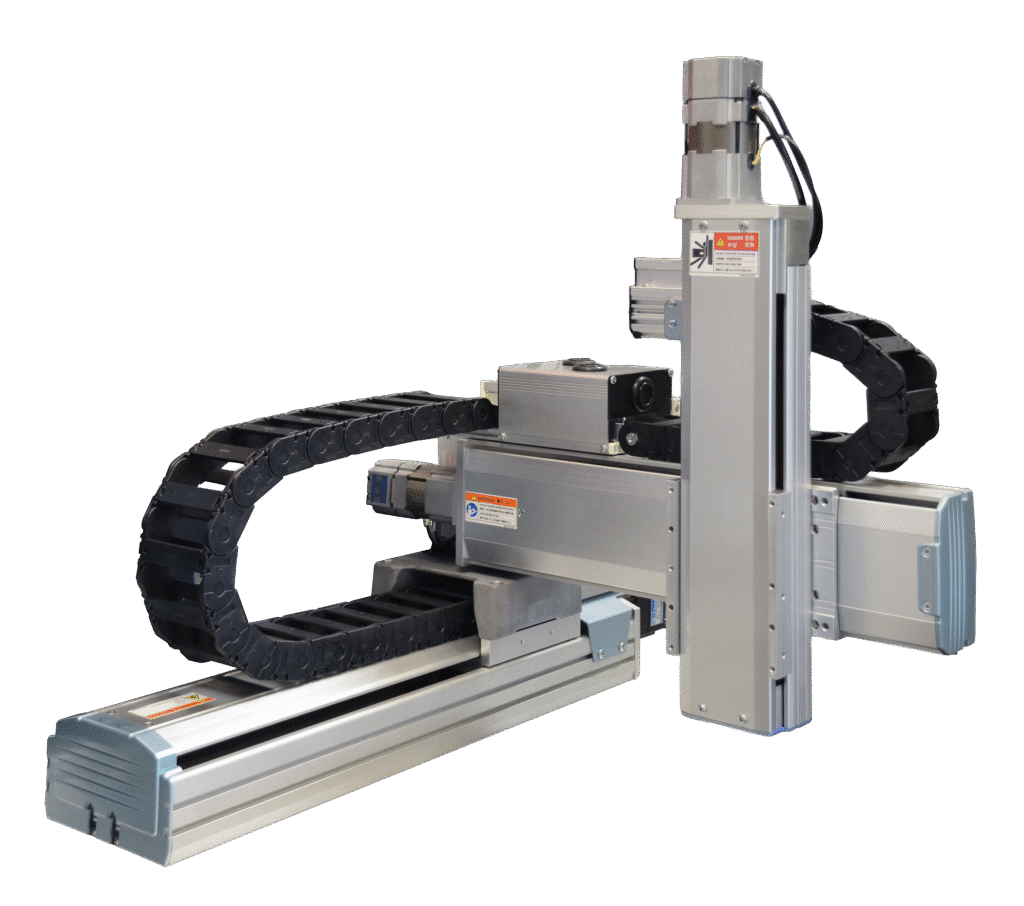
This Cartesian robotic contains actuators and linear slides from PHD. Such phases are fairly modular and significantly widespread in packaging. Supply: PHD Inc.
Actually, some suppliers supply motorized axes and movement options for each robotic kind utilized in industrial purposes. Granted, low-cost variations might prioritize use of engineered plastic elements (additionally provided individually) so that they’re not usable for all purposes.
That stated, many of those options work in analysis, meals and beverage, merchandising, shopper service, laboratory automation, and different cost-sensitive automation.
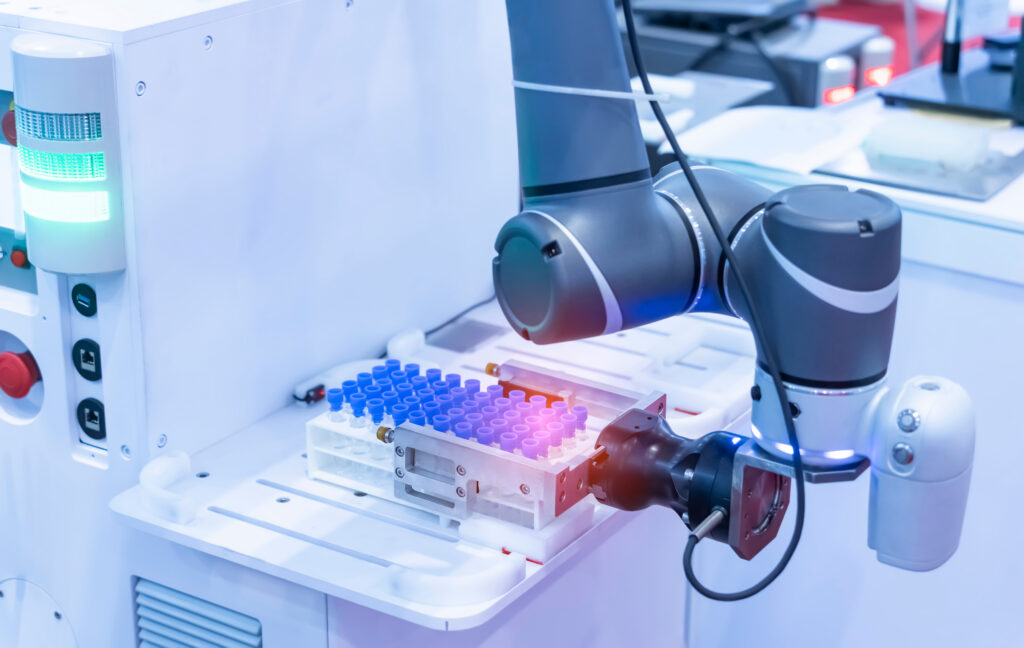

A light-weight industrial robotic arm with a check tube. Supply: Adobe Inventory
Stepper motors (and particularly closed-loop steppers) are additionally appropriate for Cartesian and SCARA-style robots utilized in mild meeting and laboratory automation — together with printed circuit board (PCB) loaders and test-fixture robots.
Closed-loop stepper motors (fitted with encoders) extra typically impart movement to joints of assemblies shifting payloads to three kg (6.6 lb.) or so — or to grippers, instrument changers, imaginative and prescient mechanisms, or feed items on welding torches.
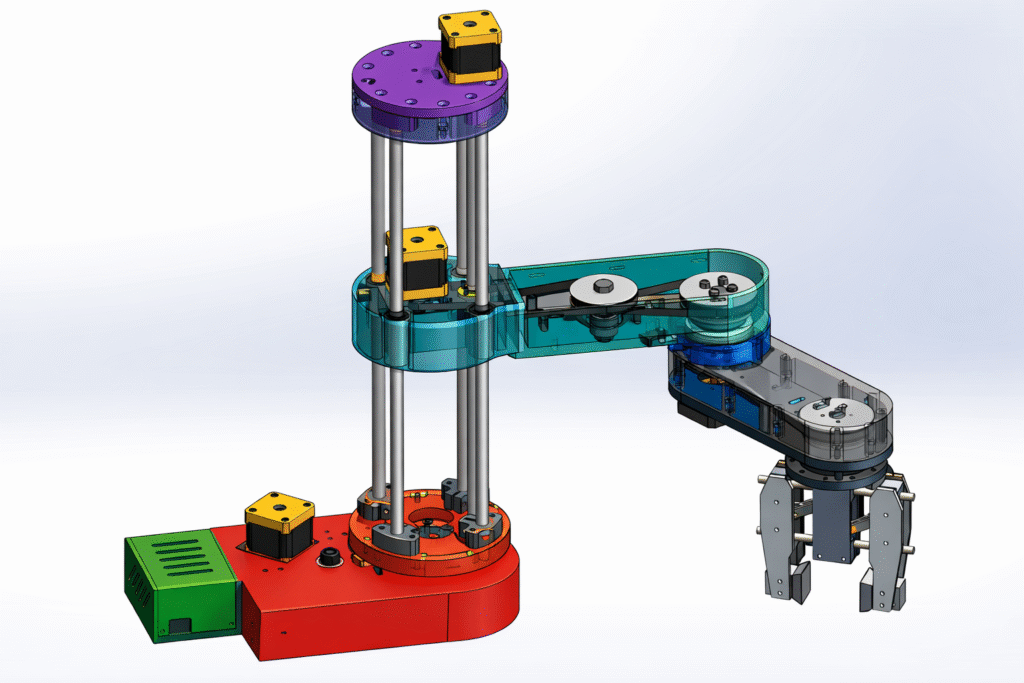
On this approachable SCARA meeting, there are stepper motors, belt drives, and a screw-driven vertical axis with plain linear guides.
Boker’s helps robotics with customized washers, spacers, and shims for bearing preload, rail alignment, gearbox spacing, end-effector mounting offsets, and sensor standoffs. These elements supply tight tolerances and repeatable materials properties. Supply: Boker’s
All the way down to the smallest elements — together with washers, spacers, shims, and fasteners. For instance, these parts maintain the meeting whereas stopping stack-up error that may trigger binding, angular misalignment, or tool-center drift.
Delta robots have distinctive kinematics and dynamics
Delta or spider robots are their very own breed with kinematics that includes NEMA stepper-based screw actuators … or belt drives on every linkage. In any other case, many industrial-grade deltas (as for pick-and-place duties) function permanent-magnet servo gearmotors (with inline helical or planetary gearing) for every parallel linkage.
Within the stainless delta robotic proven under, linkages immediately connect to servomotor output shafts. Gear ratios are low as a result of the meeting itself imparts excessive dynamics.
For gearing in delta robots, helical gearing minimizes vibration, however planetary gearing is particularly power-dense.
Typical robotic arms have six levels of freedom
Articulated six degree-of-freedom (DoF) robotic arms are what most laymen image when requested to conjure aa industrial robotic arm. These have linkages in sequence with work envelope constrained by the joints. They’re outlined by the top effector’s most X-Y-Z attain together with θX, θY, θZ ranges.
It’s widespread to make use of shoulder-elbow-wrist analogies to reference levels of freedom. A straightened elbow joint places the wrist at its furthest from the bottom — and the top effector ready of decreased usefulness. A bent elbow joint brings the end-effector nearer to its base for extra orientation vary.
Articulated robots excel at maneuvering workpieces by way of nonaligned stations and surfaces.
For six-D0F robotics (in addition to SCARAs that we’ll cowl subsequent) each joint has a set nominal repeatability. Nonetheless, general repeatability on the finish effector relies on its place in area with furthest reaches having the worst values. So, workcell structure is finest when objects are properly throughout the arm’s attain and never requiring any joints to imagine a completely straightened posture.
Movement in SCARA programs

SCARA robots have three or four-axis kinematics and management {hardware} for cupboard or DIN-rail set up. They excel in pick-and-place laboratory purposes. Supply: igus
Selective compliance meeting robotic arms (SCARA) are one other kind of articulated system with linkages in sequence. These lead for pick-and-place duties shifting workpieces from one conveyor or one other flat floor to a different — particularly if the workcell permits for the SCARA to be centrally positioned. They’re able to modest to average throughput and the place set up gained’t justify a number of customization — insertion or press-fit capabilities, for instance.
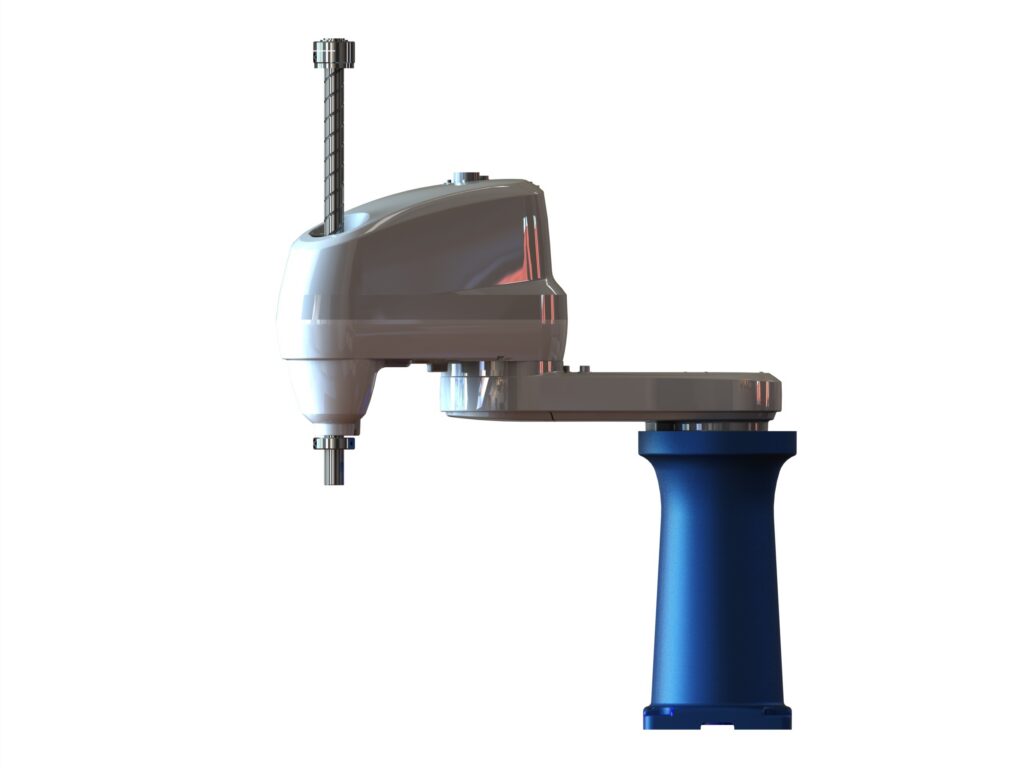

All-in-one SCARAs compete in opposition to Cartesians and serve mid-range purposes.
SCARAs could be procured as off-the-shelf, three or four-DoF options … or the kinematics lend themselves to in-house builds.
One other profit: SCARAs, like different articulated robotics, typically have handy passthroughs for feeding energy, encoder alerts, I/O wiring, and pneumatic traces from the bottom to the top effector.
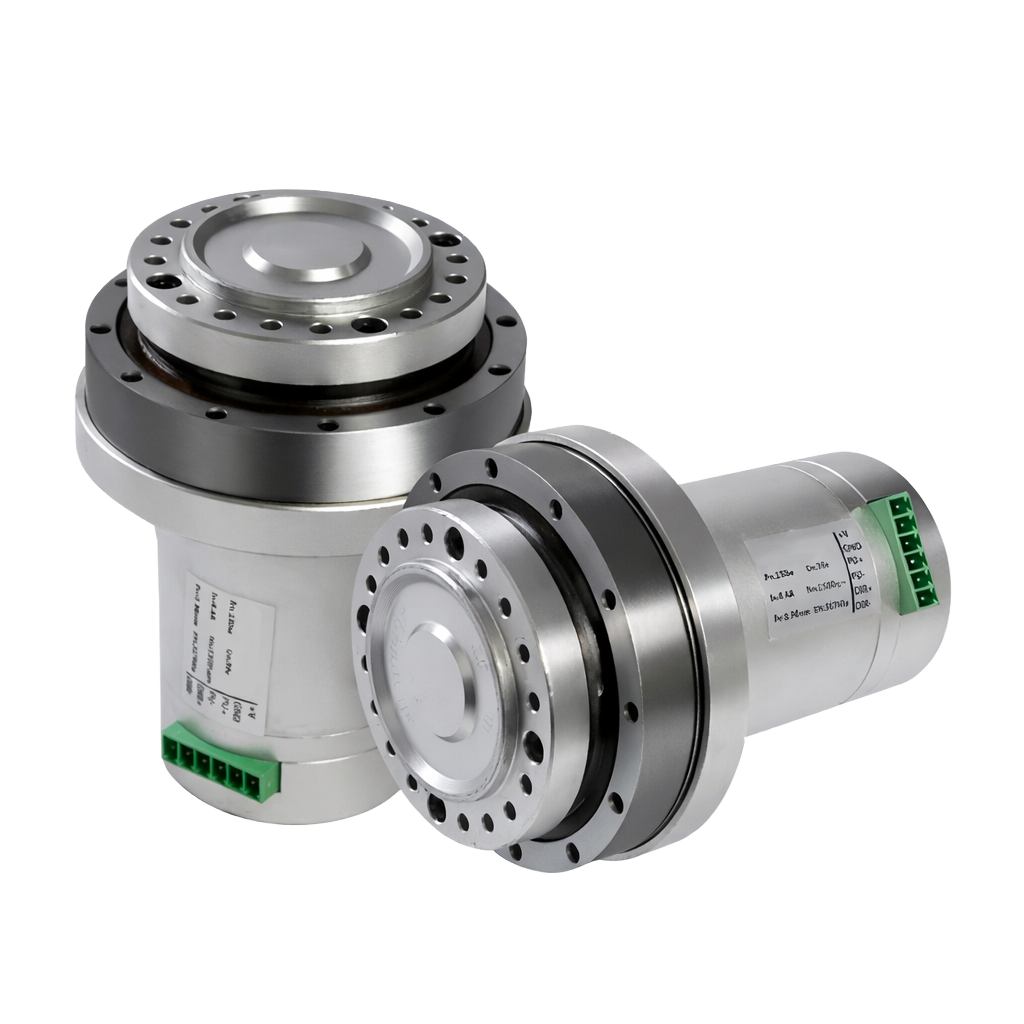

Industrial SCARA joints usually embody ac servomotors with absolute encoders for place suggestions even when important energy is reduce and restored. Encoders with out batteries can assist make the SCARA compact. Much more compactness (and attain envelope) is feasible with a well-integrated joint stack — and a motor, bearing, and equipment service having minimized axial size.
Planetary gearheads impart torsional stiffness and effectivity with compactness to suit inside joints. There’s no elastic windup like that related sure strain-wave gears. So, the controller can keep excessive repeatability with out aggressive compensation algorithms.
Additionally widespread are security brakes on the extremity joints (J3 and J4). The Z axis (as in a typical Epson robotic) makes use of a ball screw with ball spline. The igus instance under is slightly bit totally different: It has a belt-driven Z axis that includes two linear guides.

This robotic has a belt-driven Z axis that includes two linear guides. Supply: igus
Editor’s notice: This text is syndicated from The Robotic Report sibling website Design World.


